Protein synthesis
1. Protein structure
1.2 Proteins
A protein is a biological macromolecule made up of one or several chains of amino acids linked to each other by peptide bonds forming a polypeptide chain.
A protein is generally termed to be chain containing a large number of amino acids, whereas a peptide rather refers to small-sized chains.
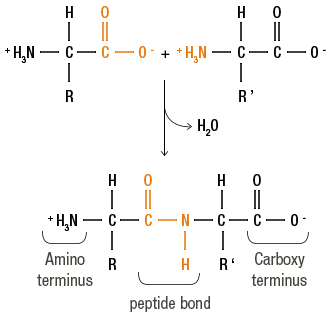
1.2.1 Peptide bond
The formation of a peptide bond is catalyzed by a ribosome.
The COOH group of the amino acid n and the NH2 group of the amino acid n+1 both participate. Accordingly, at each end of protein is found:
The NH2 group or N-terminus of the protein (next to the first amino acid).
The COOH group or C-terminus of the protein (next to the last amino acid).