DNA and genomes
1. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
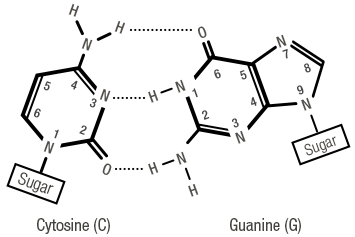
Figure 7: Bases matching with non-covalent hydrogen bonds
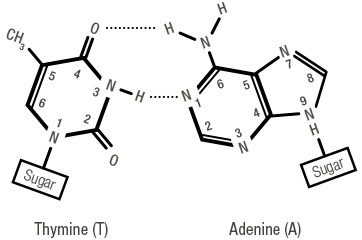
Figure 8: Bases matching with non-covalent hydrogen bonds
1.3 Double-stranded DNA
Matching of nitrogenous bases:
DNA is generally double-stranded. Matching between 2 strands of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) follows 4 rules:
Nitrogenous bases are complementary: Purine matches with Pyrimidine. Adenine matches with Thymine, and Guanine matches with Cytosine.
Matching is achieved with non-covalent hydrogen bonds: Adenine - Thymine (2 hydrogen bonds) and Guanine - Cytosine (3 hydrogen bonds).
The 2 strands are in opposite directions: Antiparallel structure.
The 2 paired DNA strands are twisted into a double helix: structure discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953.