DNA and genomes
1. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
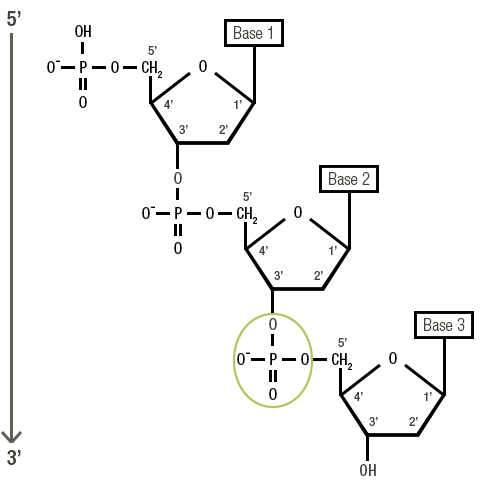
1.2 Phosphodiester bond
The Phosphodiester bond allows nucleotides to polymerise and form a DNA strand.
It is a bond between 2 nucleotides of the hydroxyl (OH) group of the 3' carbon from a nucleotide, and of the phosphate group of the 5' carbon from the next nucleotide.
A chain or (strand) of DNA is thus obtained.
Note: nitrogenous bases are not part of a phosphodiester bond.
A DNA strand has two ends, each with very different properties:
5' end free phosphate (the first nucleotide)
3' end free hydroxyl group (the last nucleotide)
By convention, a DNA strand is always read from 5' to 3'.